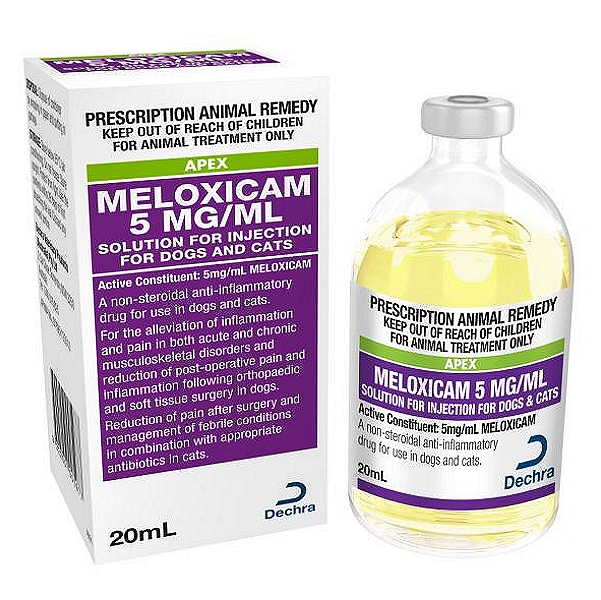
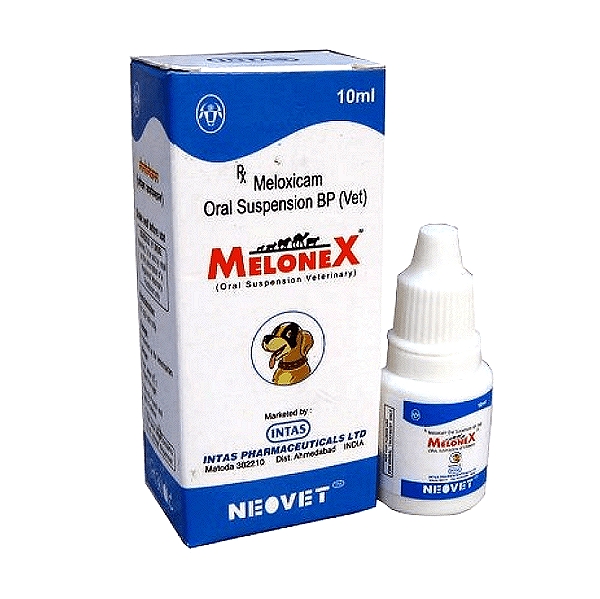
Meloxicam Injection is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to control of pain and inflammation in dogs, cats, cattle, swine, sheep, and goats.
INDICATIONS
for Dogs
- Osteoarthritis: It is indicated for the management of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
- Surgical Support: Used for the alleviation of pain after orthopedic and soft tissue surgeries.
- Acute/Chronic Conditions: Indicated for the suppression of inflammatory processes and pain in musculoskeletal system involvement.
for Cats
- Postoperative Pain Control: Specifically indicated for controlling pain and inflammation after:
- Orthopedic surgery.
- Ovariohysterectomy (spaying).
- Castration (neutering).
- Fever Management: In some jurisdictions, it is indicated for the management of febrile conditions, often in combination with antibiotics.
- Repeated use in cats is associated with acute renal failure and death; it should not be followed by additional oral or injectable doses.
for Livestock & Equine: Indications include mastitis, pneumonia, colic, and laminitis in cattle, horses, sheep, and goats.
ADMINISTRATION
- Dogs: Veterinary meloxicam injection can be administered subcutaneously or intravenously. After an initial period, treatment typically continues with an oral suspension.
- Cats: Subcutaneous administration only. Approved for a single, one-time dose in this species.
- Cattle: The injection is administered as a single dose either subcutaneously or intravenously.
- Swine: In swine, the injection is administered as a single intramuscular dose.
- Sheep: Veterinary meloxicam injection is administered as a single subcutaneous injection, commonly in the neck area behind the ear.
Guidelines
- Dosing Accuracy: Using a graduated syringe is important for accurate administration, especially in smaller animals.
- Timing: For surgical procedures, administration may occur around the time of anesthesia induction.
- Hydration: Ensuring the animal is well-hydrated before administration can help mitigate the risk of renal complications.
- Safety: Should not be given at the same time as other NSAIDs or corticosteroids.