Rabies Virus Vaccine
In Stock
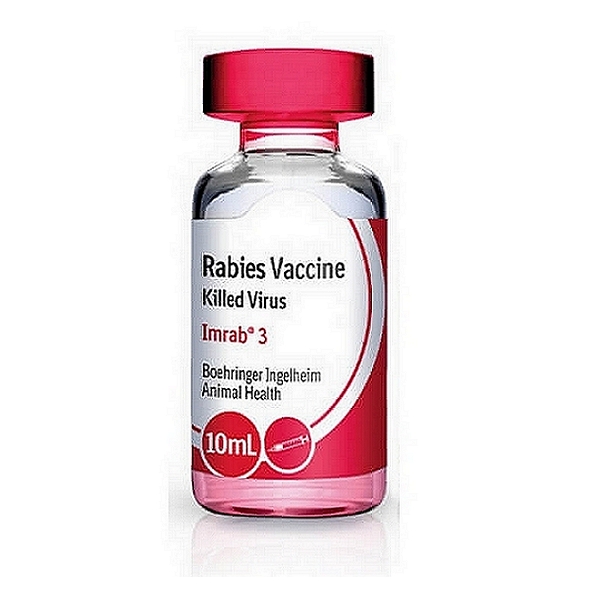
IMRAB 3 Rabies Virus Vaccine
Boehringer's IMRAB 3 Rabies virus vaccine is administered to healthy dogs, cats, ferrets, cattle, horses, and sheep that are at least 12 weeks of age, against the Rabies virus. The duration of immunity is 3 years for cats, dogs, and sheep, and 1 year for ferrets, cattle, and horses.Categories: Antivirals, R, Vaccines